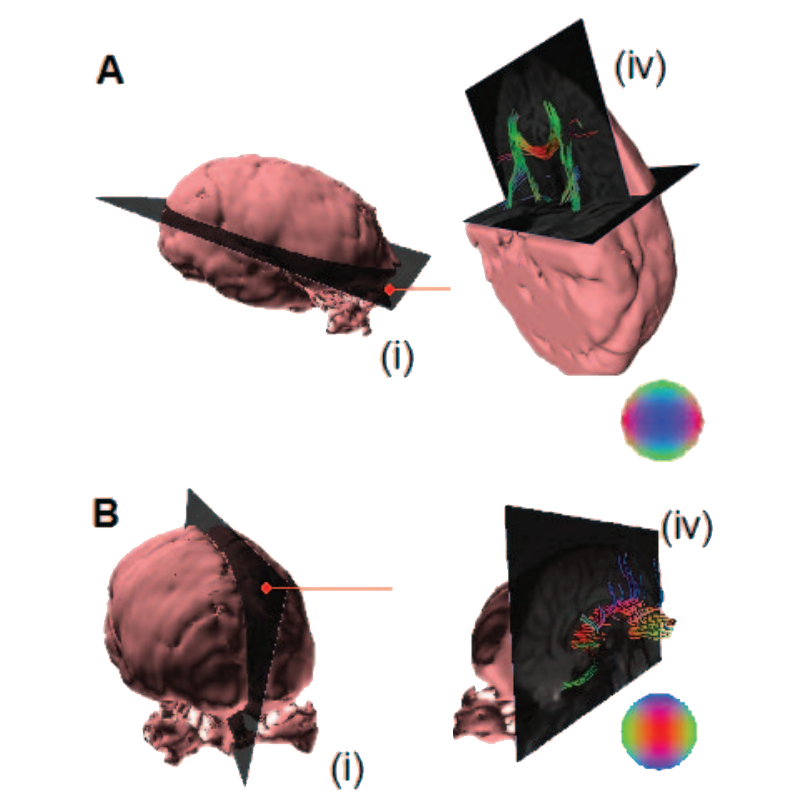
A physical basis for multi-fiber reconstruction from DW-MRI data
In Proceedings of ISBI09: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, June 28-July 1, 2009, pp. 626-629. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2009.5193125
Description
Recently various mathematical models have been proposed to model the signal attenuation obtained from Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DW-MRI). Though effective to various extents, almost all of the existing methods involve model parameters which are abstract mathematical quantities without any tangible connection to physical quantities (e.g. the b-value, gradient pulse duration, pulse separation etc.) involved in the DW-MRI acquisition process. To address this disconnect, in this paper, we present a multi-compartmental model which uses a physical model for restricted diffusion in the cylindrical geometry as the constituent basis function for multi-fiber reconstruction. Through extensive experiments on synthetic data we establish the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art techniques in terms of fiber orientation detection accuracy. We also present detailed results using human and rat brain data and demonstrate that our method leads to meaningful multi-fiber reconstruction even in the case of real data.
Additional information
| Author | Kumar, R., Barmpoutis, A., Vemuri, B. C., Carney, P., Mareci, T. |
|---|---|
| Journal | In Proceedings of ISBI09: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging |
| Year | 2009 |
| Month | June 28-July 1 |
| Pages | 626-629 |
| Publisher | IEEE |
| DOI |
Citation
Citation
BibTex
@article{digitalWorlds:162,
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2009.5193125},
author = {Kumar, R. and Barmpoutis, A. and Vemuri, B. C. and Carney, P. and Mareci, T.},
title = {A physical basis for multi-fiber reconstruction from DW-MRI data},
journal = {In Proceedings of ISBI09: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging},
month = {June 28-July 1},
year = {2009},
pages = {626-629}
}